Abstract
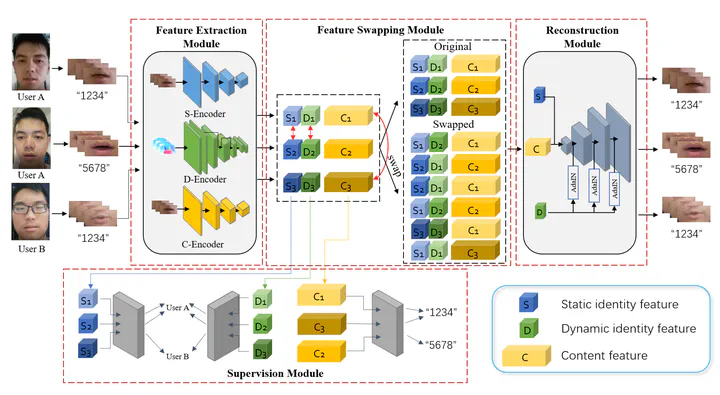
Recent studies have shown that lip shape and movement can be used as an effective biometric feature for speaker authentication. By using random prompt text scheme, lip-based authentication system can also achieve good liveness detection performance in laboratory scenarios. However, due to the increasingly widespread mobile application, the authentication system may face additional practical difficulties such as complex background, limited user samples, etc., which will degrade the authentication performance derived by current methods. To confront the above problems, a new deep neural network, i.e. the Triple-feature Disentanglement Network for Visual Speaker Authentication (TDVSA-Net), is proposed in this paper to extract discriminative and disentangled lip features for visual speaker authentication in the random prompt text scenario. Three decoupled lip features, including the content feature inferring the speech content, the physiological lip feature describing the static lip shape and appearance and the behavioral lip feature depicting the unique pattern in lip movements during utterance, are extracted by TDVSA-Net and fed into corresponding modules to authenticate both the prompt text and the speaker’s identity. Experiment results have demonstrated that compared with several SOTA visual speaker authentication methods, the proposed TDVSA-Net can extract more discriminative and robust lip features which boost the content recognition and identity authentication performance against both human imposters and DeepFake attacks.
Type
Publication
In IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology
In this paper, we proposed a visual speaker authentication system using the random prompt text scheme to meet the requirements of mobile applications. Lip features are disentangled into three parts, i.e. the static identity features, the dynamic identity features and the content features by the proposed TDVSA-Net. The experiment results show that the content features obtained the lowest WER in speaker- independent lip-reading compared with other lipreading models, and the identity features had comparable performance with the state-of-the-art methods on detecting human imposters and DeepFake imposters and exhibits more robustness when facing different image qualities. Therefore, our VSA system can be a feasible solution for today’s widely used mobile applications.