Fine-Grained Lip Image Segmentation using Fuzzy Logic and Graph Reasoning
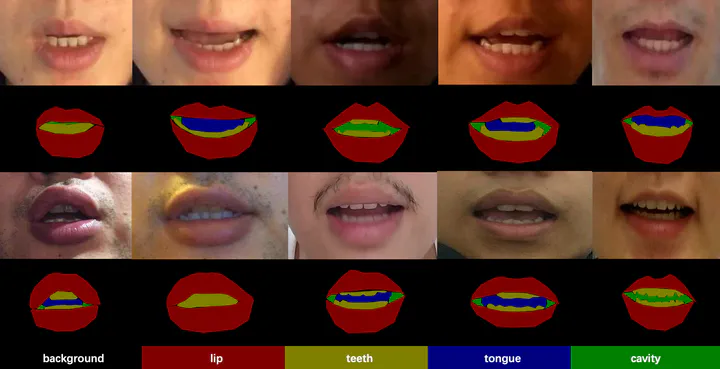
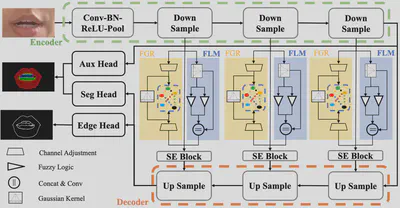
In this paper, we proposed a new lip segmentation method based on fuzzy convolutional neural network with graph reasoning that can learn high-level semantics. The fuzzy learning module and the fuzzy graph reasoning module help the deep convolutional neural network to handle uncertainties around ambiguous boundaries, capture global information, and improve multi-class lip region segmentation. In addition, a fine-grained lip region dataset is released for multi-class segmentation studies. Our proposed approach achieved satisfactory performance on the test set, with 94.36% pixel accuracy and 74.89% mIoU. The experiment results have demonstrated that the proposed method can be applied in many lip-related applications to obtain accurate and robust lip region segmentation in natural scenes.
However, the proposed network cannot achieve satisfactory results in certain scenarios, specifically in cases of occlusion or extreme lighting conditions. This limitation can be attributed to the FLRSeg dataset, which is derived from the VSA dataset that was collected for speaker authentication and thus required unobstructed lip movements. In our future work, we will further improve the segmentation performance in various situations and explore the potential of leveraging the segmentation results in downstream tasks, such as lip reading and visual speaker authentication, to enhance performance and accelerate converge.